Technical Architecture
1 Architecture
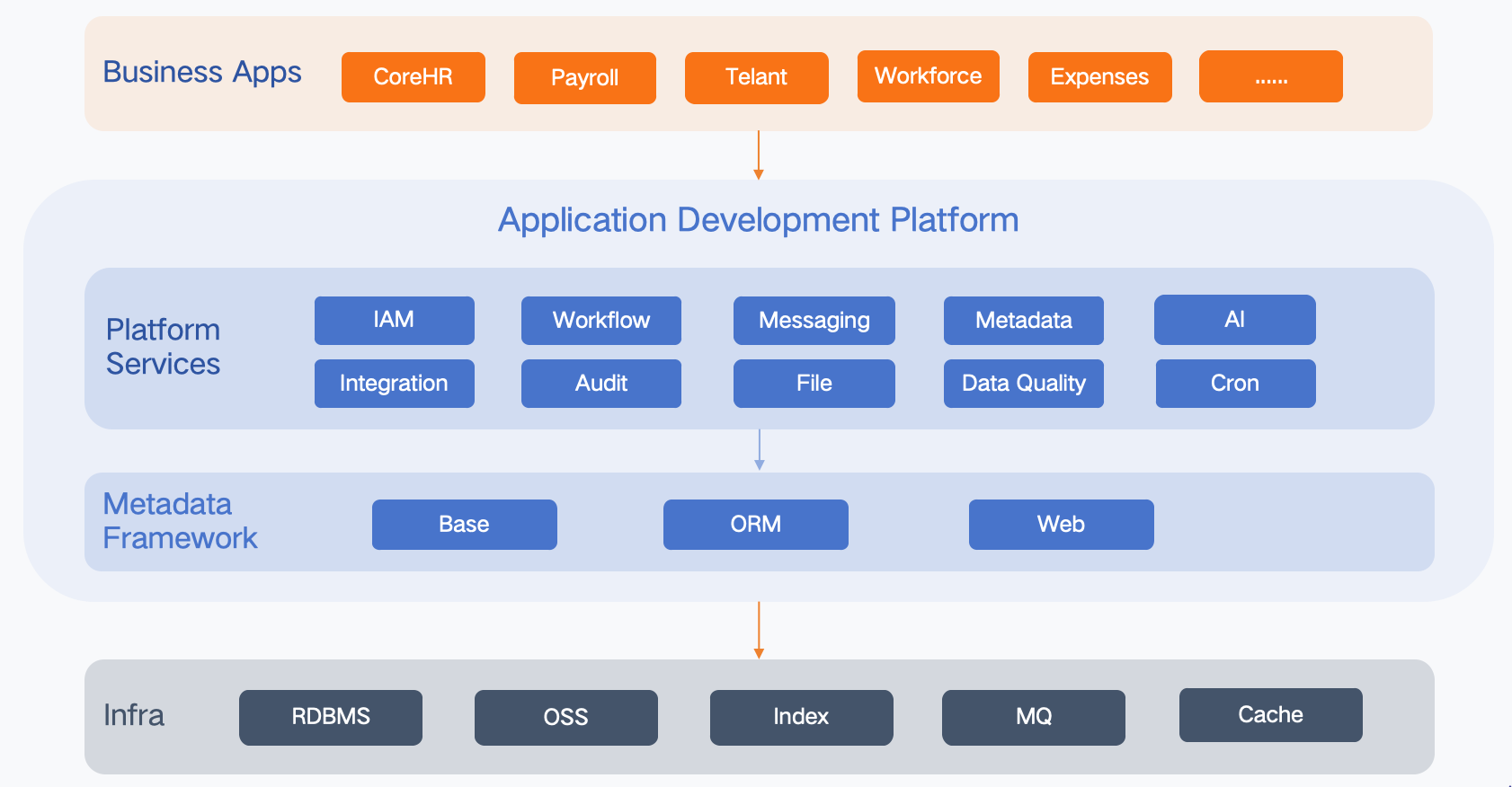
This architecture is centered on the Softa Application Development Platform, following a top-down layered model.
The top layer is Business Apps, such as CoreHR, Payroll, Talent, Workforce, and Expenses, which directly serve business scenarios and end users.
The middle layer provides platform capabilities and consists of:
Platform Services – common services including IAM, Workflow, Messaging, Metadata, AI, Integration, Audit, File, Data Quality, and Cron, offering unified capabilities for all applications;
Metadata Framework – Base, ORM, and Web components that support model-driven development and rapid application building.
The bottom layer is Infra, including RDBMS, OSS, Index, MQ, and Cache, providing storage, messaging, and caching support.
Together they form a structure of Business Apps → Platform Services → Metadata Framework → Infra, achieving decoupling between business and technology and enabling fast delivery and continuous scalability.
2 Data Architecture
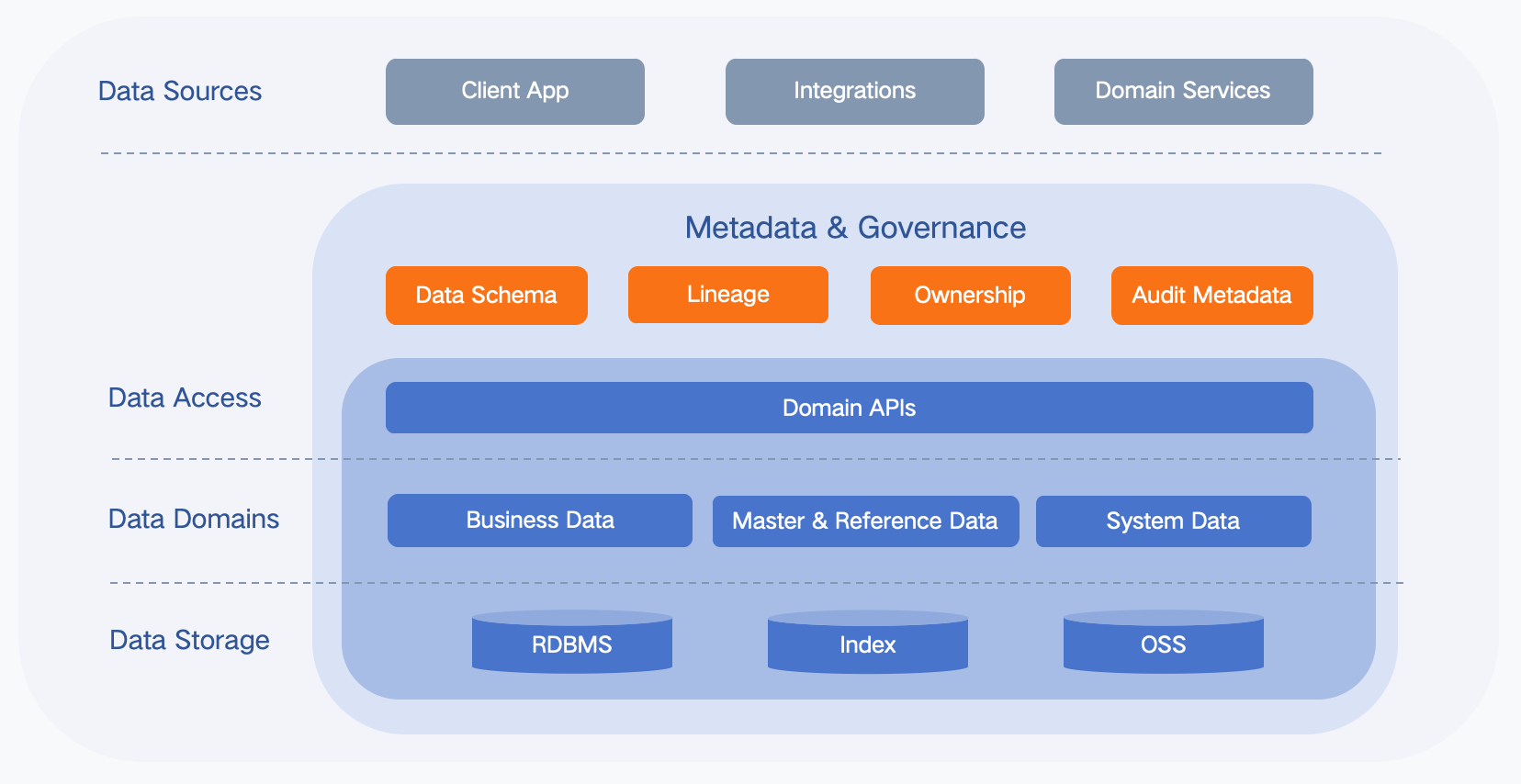
This architecture follows a model of Governance-Driven + Domain Access + Multi-Model Storage. Metadata acts as the central hub to decouple data sources, domain services, and physical storage.
The structure consists of:
-
Vertical dimensions: Data Sources → Data Access → Data Domains → Data Storage
-
Horizontal layers: Metadata & Governance → Domain APIs → Data Domains → Storage
Core principle: All data must be accessed through Domain APIs, governed by metadata, and abstracted from storage.
2.1 Core Layers
(1) Metadata & Governance
Central control layer responsible for:
- Data Schema – unified models
- Lineage – data flow tracking
- Ownership – responsibility definition
- Audit Metadata – compliance records
This layer defines how data is understood and managed, not where it is stored.
(2) Domain APIs
The only entry for data access:
- Unified domain interface
- Shielding storage diversity
- Carrying business rules
- Collaborating with governance
It is the bridge between governance and applications.
(3) Data Domains
Data is organized into:
- Business Data
- Master & Reference Data
- System Data
Each domain has its own lifecycle and policy.
(4) Data Storage
Multi-model persistence:
- RDBMS – structured data
- Index – search acceleration
- OSS – unstructured objects
Fully abstracted by Domain APIs.
2.2 Consumers and Ingress
- Client App
- Integrations
- Domain Services
Access path: Data Sources → Domain APIs → Governance → Storage
2.3 Characteristics
- Governance before access
- Single domain entry
- Pluggable storage
- Traceable & auditable
- Clear responsibilities
3 Technical Components
Frontend Components
- React …
Backend Components
- Java 25 LTS
- SpringBoot 4.0.2
- Redis
- ElasticSearch …