Multi-Tenancy Support
1. Introduction to Multi-Tenancy
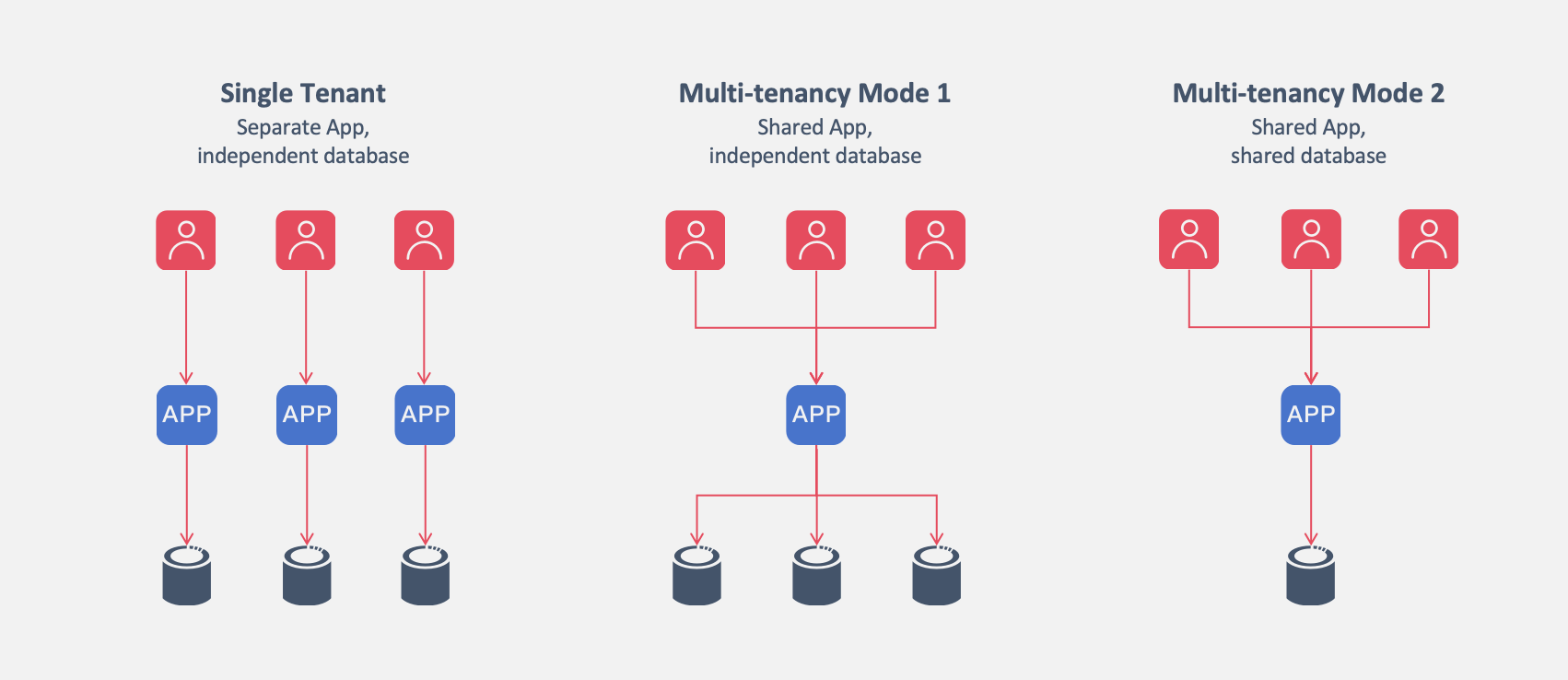
Multi-tenancy is a software architecture pattern that allows multiple tenants to share a single system instance while ensuring data isolation between tenants. This enables resource reuse, unified upgrades and maintenance, standardized data analysis, and large-scale promotion.
Softa natively supports two multi-tenancy modes: shared application with shared database mode, and shared application with independent database mode. Once multi-tenancy is enabled, data is automatically isolated by tenant.
2. Enabling Multi-Tenancy
2.1 Multi-Tenancy Mode 1: Shared Application with Shared Database
Enable multi-tenancy by setting system.multi-tenancy.enable=true in the configuration file. For example:
system:
multi-tenancy:
enable: true2.2 Multi-Tenancy Mode 2: Shared Application with Independent Database
Since Softa supports dynamic multi-data sources, the UserInfo object includes tenantId and datasourceKey fields.
When a user logs in, these fields can be populated in the ContextInterceptor interceptor implementation.
Enable multi-tenancy in the configuration file by setting system.multi-tenancy.enable=true, and also enable dynamic multi-data source with the mode set to multi-tenancy-isolated.
system:
multi-tenancy:
enable: true
spring:
datasource:
dynamic:
enable: true
# mode: read-write-separation, switch-by-model, multi-tenancy-isolated, multi-datasource(default)
mode: multi-tenancy-isolated
datasource:
tenant1:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo
username: user0
password: pass0
tenant2:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1
username: user1
password: pass1
tenant3:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2
username: user2
password: pass23. Multi-Tenancy Data Model
Once multi-tenancy is enabled, data isolation can be configured at the model level.
Conditions for Enabling Tenant Isolation in Models:
- Set the model metadata
multiTenant = true. ThismultiTenantattribute controls which data models are subject to tenant isolation. Models withmultiTenant = falsecan be shared across tenants. - Add a
tenantIdfield to the model. This field is globally read-only and is populated with thetenantIdof the current user upon creation. Modifying this field is not allowed.
4. Data Isolation Strategies Between Tenants
Once multi-tenancy is enabled, the ORM enforces strict isolation and validation. The current user’s tenantId is recorded in the context (user.tenantId).
4.1 Simple Queries
The ORM automatically appends a tenant filter condition to the WHERE clause:
tenant_id = user.tenantId4.2 JOIN Queries
The tenant filter condition is automatically appended to both the main table and the related tables without requiring developer intervention:
t0.tenant_id = user.tenantId AND t1.tenant_id = user.tenantId4.3 Data Creation
During data creation, the ORM automatically populates the tenantId field:
tenantId = user.tenantIdIf the client specifies a tenantId that differs from the current user’s tenantId, the system will throw an exception, indicating a potential unauthorized access attempt.
4.4 Data Updates
Since the tenantId field in the data model is read-only, the ORM ignores any attempts to modify the tenantId.
4.5 Data Deletion
Before deletion, the ORM checks the data scope, ensuring that only data belonging to the current user’s tenant can be deleted.
5. Multi-Tenant System Operations Platform
Operating a multi-tenant system requires cross-tenant data access for tenant management, data configuration, and analysis.
5.1 Operations Platform Without Tenant Isolation
The operations platform should deploy separate front-end and back-end services with a unique access domain. In this system, multi-tenancy should not be enabled, i.e., system.multi-tenancy.enable = false.
5.2 Tenant Properties in the Operations Platform
In the operations platform, tenants are treated as an attribute of data authorization. The tenantId field in data models serves only as a cross-tenant data authorization condition. Even if the data model includes a tenantId field, it is not subject to multi-tenancy restrictions enforced by the ORM layer.